For those who work in electrical design, a prominent concern is circuit protection. While a lot of circuit protection technologies exist, it is most common to guard against overcurrent situations. Overcurrent protection can be achieved by incorporating fuses or circuit breakers along the primary power feed. But which of these devices do you use for branch protection or for supplementary protection? The following information should help you understand UL489 and UL1077 requirements so that you can know the difference between branch and supplementary protection.
UL 489 Rated Circuit Breakers
In general, circuit breakers protect a circuit from any damage when there is an over-current situation. The circuit breaker design allows for it to be reset in the event that overcurrent causes it to trip.
In most cases, a circuit breaker can also double as a power disconnect, which makes them very convenient for use with any equipment that may require regular service.
Two common types of UL 489 circuit breakers are miniature circuit breakers and molded case circuit breakers (MCCB).
- The miniature circuit breakers protect feeder, branch and control circuits from overload current. They are also space-saving breakers in single-, two- and three-pole configurations.
- The molded case circuit breakers provide branch or feeder circuit protection against overload or short circuits using thermal-magnetic trip units to sense both temperature and current to operate the breaker.
UL 1077 Rated Supplementary Protectors
Supplementary protectors are basically a circuit breaker designed to meet the UL 1077 requirements. These breakers supplement circuit protection by providing over-current protection where branch circuit protection is already in place or not required. Just like circuit breakers, they are also designed to be reset in the event that overcurrent causes it to trip.
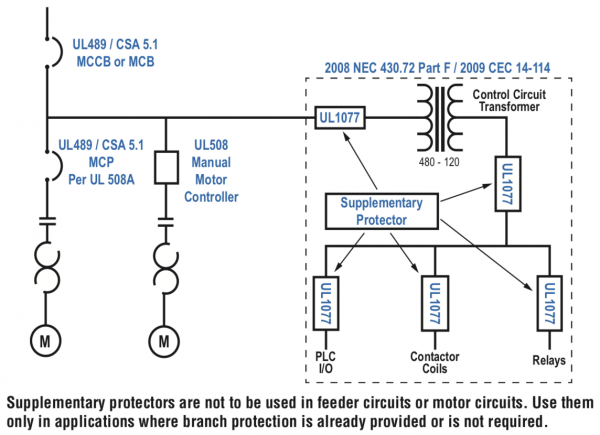
See NEC Sections 100, 430 and 409 for definitions.
The proper sizing of an overcurrent protection device is the responsibility of the customer and should be determined using the application standards of the NEC (National Electric Code), CEC (Canadian Electrical Code) or other applicable standards. Per the fine print note of 2008 NEC Section 100, “A current in excess of rating may be accommodated by certain equipment and conductors for a given set of conditions. Therefore, the rules for overcurrent protection are specific for particular situations.”

What You Need to Know and Look For in Specifications
Certifications – Standards – Acceptance
UL489 Branch Protection
- UL489 Listed or Recognized
- CSA C22.2 No. 5
- International ratings available depending on breaker type
UL1077 Supplementary Protection
- UL Recognized under UL1077
- CSA 22.2 No. 285
- IEC 60947-2 or IEC 898
Function
- Opens automatically on Overload and Short Circuit when properly applied within its ratings
- Protects wire and cable against Overload and Short Circuit
- Provides additional equipment protection where branch circuit protection is already provided or not required
- Not suitable for the protection of branch circuit conductors
Applications
- Branch circuit protection in control panels, panelboards, switchboards and motor control centers
- Motor overload and motor short circuit protection (UL489 Recognized motor circuit protectors) for control panels and motor control centers
- Used within appliances or other electrical equipment such as control circuits, control power transformers, relays, PLC I/O points and lighting circuits
- Ideal replacement for fuses that are applied as supplementary protection
Features
- Bolted down or DIN-rail mounted
- External handle mechanisms available
- Field mounted accessories
- Stand alone branch circuit protection
- Various levels of protection (curve type)
- High voltage and interruption levels (up to 100 kAIC @ 480V)
- DIN-Rail mounted
- Field mounted accessories
- Current limiting
- Various levels of protection (curve type)
- 10 kAIC @ 240 VAC
- 6 kAIC @ 277 VAC and 5 kAIC @ 480 VAC
- 10 kAIC @ 65 VDC
kAIC = thousands of Amps interrupt capacity
Summary
A Supplementary Protector can’t be used for Branch Circuit Protection. Understanding the difference between Branch Circuit Protection and Supplementary Protection helps to ensure their proper use. To learn about the different types of circuit breakers as well as where and when they should be used, check out this video.