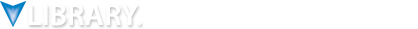Anyone who has ever observed a modern factory in action, whether in person or perhaps via an episode of the “How It’s Made” documentary television series, is aware of just how impressive machine automation can be. This is especially the case when witnessing robotic arms and other machine motion control, as mechanical apparatus and payloads shuttle rapidly and precisely from point to point.
Within the industrial automation arena, the term “motion control” usually refers to the use of an electric motor—either a servo or stepper motor—to precisely drive the position, velocity, and acceleration of a physical system, or to exert a specific amount of torque on that system. There are other motion control methods as well—pneumatics are economical, and hydraulics can provide great force— but electric motors often provide the right balance of accuracy, speed, power, durability, and operating cost.
There are many types of electric motors and motor systems that can operate at fixed speeds, and many that can provide excellent variable-speed control, but to be considered ‘motion control’ the motor must be capable of accelerating at a specified rate, to a specified speed and then decelerating (again at a known rate) to stop at an exact position.
Several technologies are relevant for the electric motors, drives, and controllers used to achieve comprehensive motion control. Additionally, the last decade has seen massive improvements in motor efficiency, drive intelligence, digital controller capabilities, and communications connectivity among these devices. Electrical motor motion control is now easier, more cost-effective, and exceedingly practical for all types of applications than ever before.

What is a Stepper Motor?
A stepper motor (sometimes called a step motor or stepping motor) is a DC motor with a fixed number of steps that make a full rotation. Read More –>

What is an AC Servo Motor?
Take a unique look at how an AC Servo Motor works. This video breaks down an AC Servo Motor and shows you a new way to visualize the magnetic fields inside the motor and how they interact. Watch Now –>
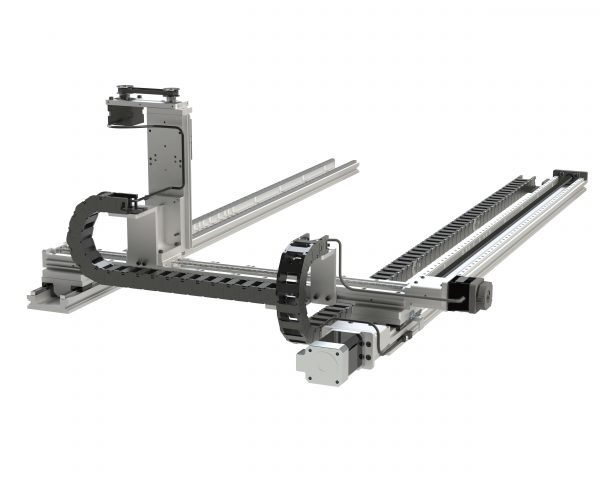

Linear Actuator Options
Linear actuators, driven with servo or stepper motors, are an effective way to implement accurate automated machine motion. Read More –>
What is an Encoder?
For determining the precise motion of industrial machinery and equipment elements, or servo motors, encoders provide a high-performance solution—but only if they are specified properly. Read More –>
What is EtherCAT?
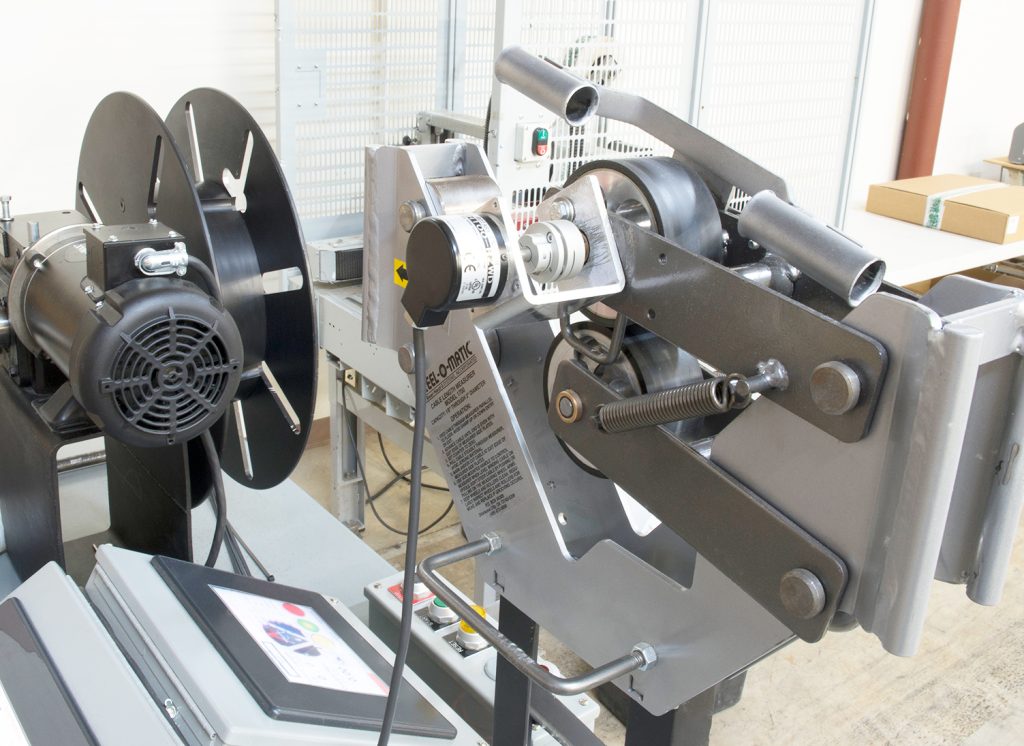
EtherCAT, which stands for Ethernet for Control Automation Technology, is a high-performance industrial network protocol based on standard Ethernet. Read More –>

White Paper: When to Use Steppers for Motion Control
Stepper motors can be the best option, even for precision motion control applications, while avoiding the expense and complexity of servo motors. Download Now –>
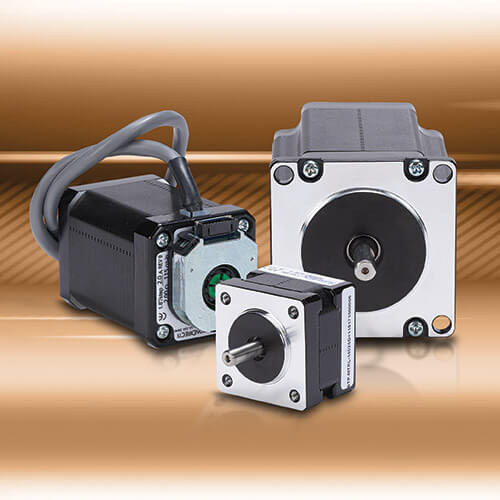

How to Control a Stepper Motor
Stepper motors use specialized control methods to achieve better precision than standard variable speed motors, while avoiding the expense and complexity of servo systems. Read More –>
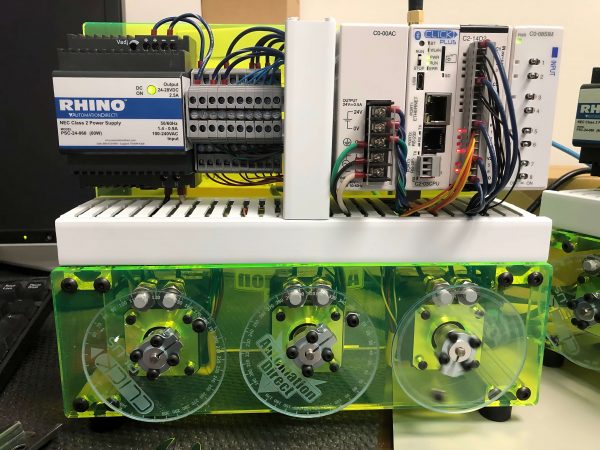

Practical Motion Control Using Micro-PLCs
Designers working on smaller automation systems can now take advantage of advanced yet economical motion control by using micro-PLCs and stepper motors. Read More –>
Simpler Servos Speed Solutions
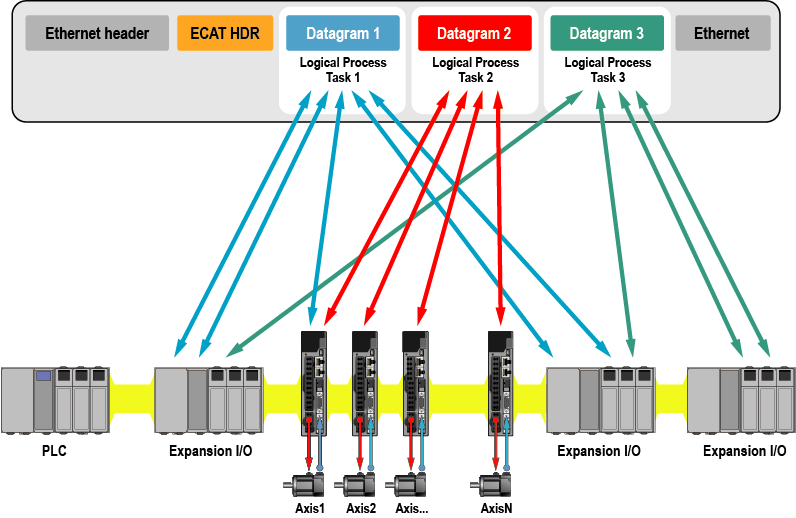
Servo systems are a leading way to implement high-performance motion control, and the latest servo drives offer functional, programming, and diagnostics capabilities to help users quickly create and commission solutions. Read More –>