+Tech TopicsAutomation NotebookDiscrete SensingIssue 25 – 2013Learning ResourcesNotebook IssueProductTechnology Brief
Encoders Explained
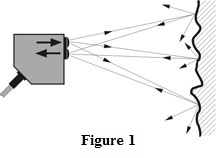
What is an Encoder? An encoder (for industrial controls) is a special sensor that captures position information and relays that data to other devices. The position information can be read in many ways (optically, magnetically, capacitively, etc.). There are two basic geometries for encoders: linear and rotary. A linear encoder typically consists of a scale…